Serotonin, oxytocin, excess dopamine, and norepinephrine are moderated with acupuncture.
(Filshie J, White A. Medical Acupuncture: A Scientific Approach. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone; 2006:75)
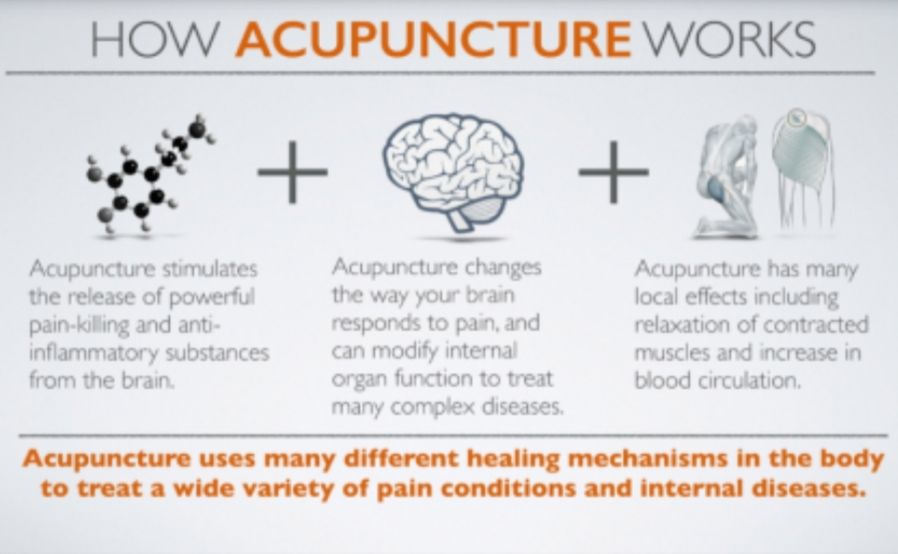
Opiod peptides stimulated through acupuncture include ß-endorphin, enkephalin, dynorphin, and orphanin.
(Filshie J, White A. Medical Acupuncture: A Scientific Approach. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone; 2006:76)
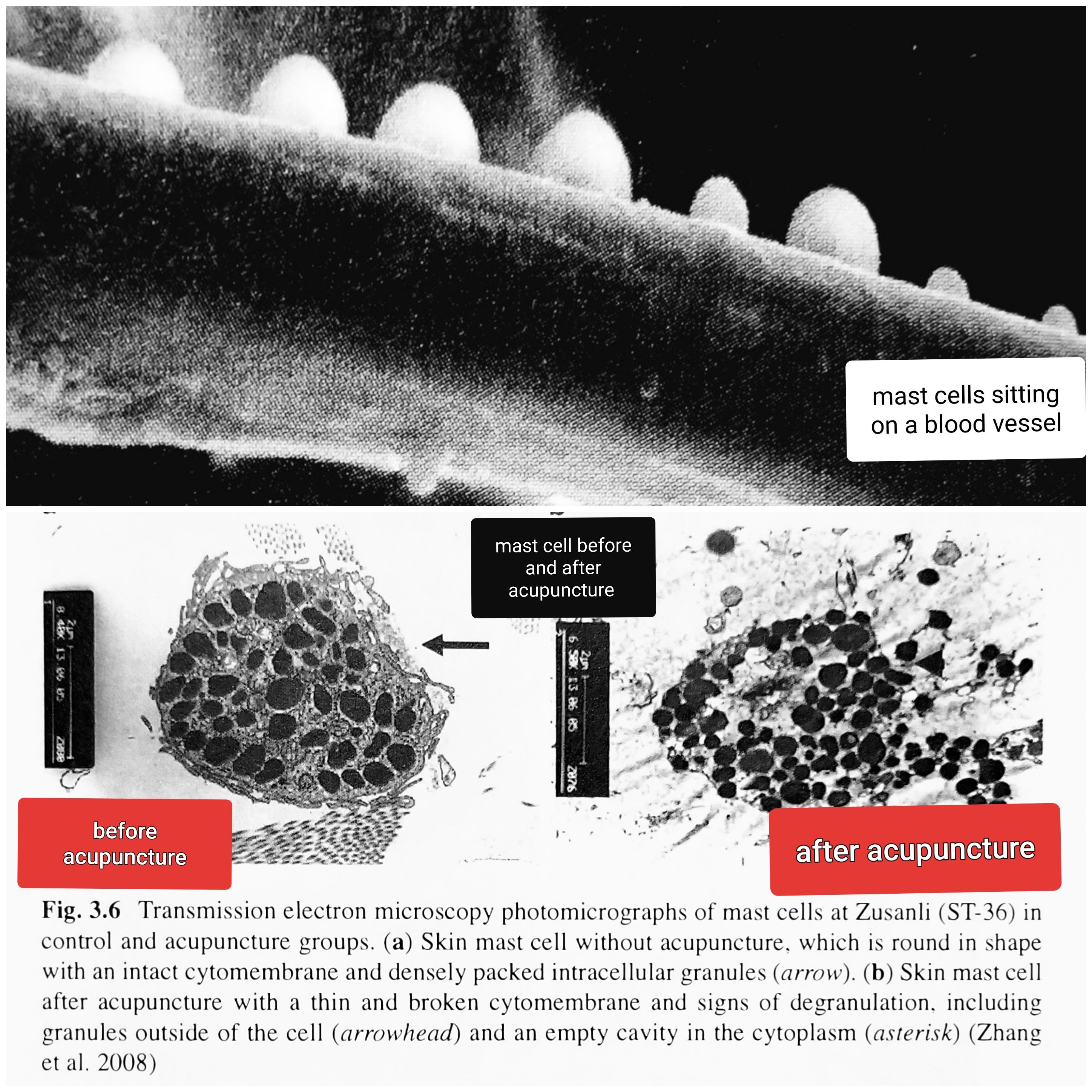
Changes in connective tissue caused by mechanical stimulation causes a reaction in an area of about 2.5cm from the needling site.
(Purves D, Augestine G, Fitzpatrick D, Hall W, LaMantia AS, White L. Neuroscience 5th edition. Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates, INC; 2012; 221)
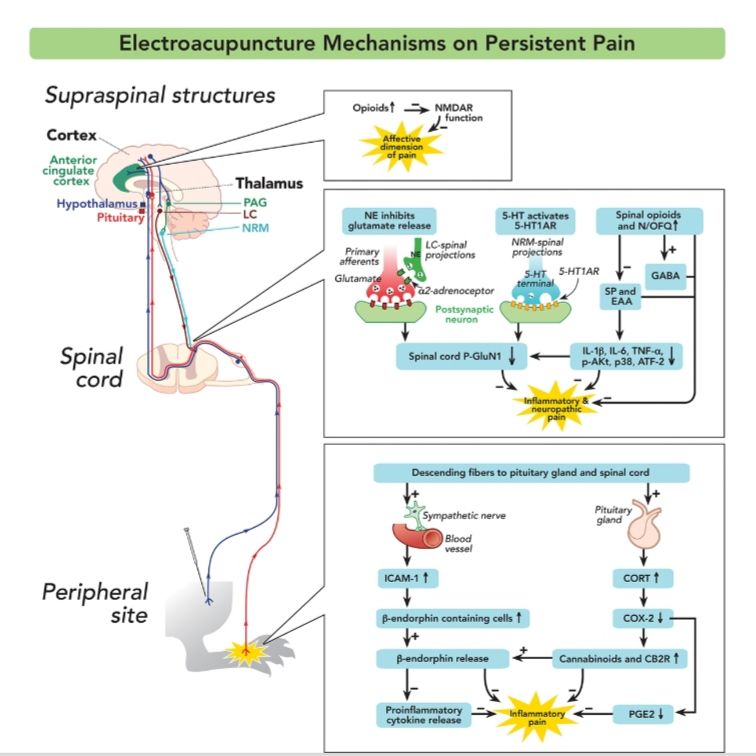
Acupuncture can control visceral (organ) afferent autonomic and sympathetic nerve.
(Filshie J, White A. Medical Acupuncture: A Scientific Approach. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone; 2006:136)
Acupuncture generally regulates a reflex response into its normal direction, as most of acupuncture's effects are on the sympathetic nerves (the exception would be S2, S3, and S4 nerves which innervates the bladder)
Pain control involves the reinforcement of segmental analgesia by activating a generalized system of extrasegmental analgesia.
(Filshie J, White A. Medical Acupuncture: A Scientific Approach. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone; 2006:108)
Opioid Peptide Metabolism and gene expression exponentially increases each time acupuncture is applied
(Filshie J, White A. Medical Acupuncture: A Scientific Approach. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone; 2006:89)
Needle retention of more than 45 minutes can be counterproductive as it can stimulate CCK (cholecystokinin) and increase pain after acupuncture.
(Filshie J, White A. Medical Acupuncture: A Scientific Approach. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone; 2006:77)
Acetylcholine
Acupuncture has been shown to influence acetylcholine (ACh) levels, a neurotransmitter involved in various physiological processes, including muscle activation, heart rate regulation, and cognitive functions. Several studies have explored the relationship between acupuncture and ACh:
1. Acupuncture and Acetylcholine Release:
A study investigated the effects of electroacupuncture (EA) on ACh release in the hippocampus and cortex of rats. The results indicated that EA increased ACh release in these brain regions, suggesting a modulatory role of acupuncture on cholinergic neurotransmission.
2. Acupuncture and Acetylcholine Receptor Expression:
Research examined the impact of acupuncture on the expression of ACh receptors in the brains of rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. The findings demonstrated that acupuncture could modulate the expression of these receptors, potentially contributing to cognitive improvements observed in such conditions.
3. Acupuncture's Effect on Acetylcholine Esterase Activity:
A study assessed the effect of acupuncture on acetylcholine esterase (AChE) activity in the brains of rats with Alzheimer's disease. The results suggested that acupuncture treatment could reduce AChE activity, leading to increased ACh levels and potential cognitive enhancement.
4. Acupuncture and Autonomic Nervous System Regulation:
Acupuncture has been associated with the modulation of the autonomic nervous system, which relies heavily on ACh for parasympathetic signaling. Studies have observed that acupuncture can influence heart rate variability and other autonomic parameters, implicating ACh in these effects.
These studies collectively suggest that acupuncture can influence acetylcholine-related pathways, potentially contributing to its therapeutic effects in various neurological and physiological conditions. However, more research is needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms underlying these interactions.
Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide (CGRP)
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a neuropeptide involved in vasodilation and pain transmission. Acupuncture has been studied for its effects on CGRP levels, particularly concerning pain modulation.
1. Acupuncture and CGRP in Pain Modulation:
A study investigated the effects of acupuncture on CGRP expression in a rat model of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain. The results indicated that acupuncture reduced CGRP expression in the TMJ region, suggesting a role in alleviating pain through modulation of this neuropeptide.
2. Acupuncture's Impact on CGRP in Migraine Models:
Research examined the effects of acupuncture on CGRP levels in a rat model of migraine. The findings demonstrated that acupuncture decreased CGRP release, which may contribute to its therapeutic effects in migraine treatment.
3. Electroacupuncture and CGRP in Neuropathic Pain:
A study explored the impact of electroacupuncture on CGRP expression in rats with neuropathic pain. The results suggested that electroacupuncture could modulate CGRP levels, offering insights into its analgesic mechanisms.
These studies highlight acupuncture's potential to influence CGRP levels, providing insight into its mechanisms for pain relief. However, further research is necessary to fully understand these interactions and their clinical implications.
Prostaglandins
Acupuncture has been studied for its effects on prostaglandins, which are lipid compounds involved in inflammation and pain regulation. Research indicates that acupuncture may influence prostaglandin levels, thereby affecting pain perception and uterine motility.
1. Acupuncture at Sanyinjiao (SP6) Point:
A study involving primary dysmenorrhea patients assessed the impact of acupuncture at the SP6 point on plasma levels of prostaglandins. The findings revealed a significant reduction in pain intensity following acupuncture; however, there were no notable changes in the plasma levels of prostaglandins (PGE₂, PGF₂α, TXB₂, and 6-keto PGF(1α)) post-treatment. This suggests that the immediate analgesic effects of acupuncture at SP6 might not be mediated through alterations in prostaglandin levels.
2. Acupuncture and Prostaglandin F2α in Menstrual Fluid:
In another study on primary dysmenorrhea, patients underwent acupuncture or massage treatments, and the levels of prostaglandin F2α in menstrual fluid were measured. Both acupuncture and massage groups exhibited a significant decrease in PGF2α levels compared to the control group, which received oral medication. This indicates that acupuncture may alleviate dysmenorrhea by modulating prostaglandin levels in menstrual fluid.
3. Electroacupuncture's Effect on Prostaglandins and Inflammatory Pathways:
Electroacupuncture was applied to rats with primary dysmenorrhea to evaluate its effect on uterine prostaglandin F2α levels, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression, and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation. The results demonstrated that electroacupuncture significantly reduced PGF2α levels, COX-2 expression, and NF-κB activation in the uterus. These findings suggest that acupuncture modulates inflammatory pathways, potentially contributing to pain relief in dysmenorrhea.
4. Acupuncture's Impact on Uterine Motility and COX-2 Expression:
Research on pregnant rats examined the effects of acupuncture at the LI-4 acupoint on uterine motility and COX-2 expression. Acupuncture led to a significant reduction in uterine motility and decreased COX-2 expression in both the endometrium and myometrium. This suggests that acupuncture may regulate uterine contractions and inflammatory responses, which could have implications for managing preterm labor.
In summary, acupuncture appears to influence prostaglandin levels and related inflammatory pathways, contributing to its analgesic effects in conditions like dysmenorrhea. However, the mechanisms may vary depending on the acupuncture point used and the specific physiological context. Further research is necessary to fully elucidate these mechanisms and optimize acupuncture's therapeutic applications.